Felix Whelan Content Uploads 2014 Genuflect 2

Download PDF Here
The Competition for Outer Space Resource and the Function of Eye Powers
by Dr Namrata Goswami
Dr. Namrata Goswami is an author, strategic analyst and consultant on counter-insurgency, counter-terrorism, alternate futures, and peachy power politics. Subsequently earning her Ph.D. in international relations, she served for nearly a decade at India's Ministry of Defence (MOD) sponsored think tank, the Constitute for Defence Studies and Analyses (IDSA), New Delhi, working on ethnic conflicts in Republic of india's Northeast and China-Republic of india border conflict. She is the author of three books, "Bharat's National Security and Counter-Insurgency", "Asia 2030" and "Asia 2030 The Unfolding Future." Her research and expertise generated opportunities for collaborations abroad, and she accepted visiting fellowships at the Peace Inquiry Institute, Oslo, Norway; the La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia; and the University of Heidelberg, Deutschland. In 2012, she was selected to serve every bit a Jennings-Randolph Senior Boyfriend at the Usa Constitute of Peace (USIP), Washington D.C. where she studied India-China border problems, and was awarded a Fulbright-Nehru Senior Fellowship that same year. Presently after establishing her own strategy and policy consultancy, she won the prestigious MINERVA grant awarded past the Office of the U.South. Secretary of Defence force (OSD) to study great power contest in the grey zone of outer space. She was also awarded a contract with Joint Special Operations University (JSOU), to work on a project on "ISIS in Due south and Southeast Asia". With expertise in international relations, ethnic conflicts, counter insurgency, wargaming, scenario building, and conflict resolution, she has been asked to consult for audiences as diverse as Wikistrat, USPACOM, USSOCOM, the Indian Military and the Indian Government, academia and policy think tanks. She was the offset representative from S Asia called to participate in the George C. Marshall European Center for Security Studies NATO Partnership for Peace Consortium (PfPC) 'Emerging Security Challenges Working Group.' She as well received the Executive Leadership Certificate sponsored by the Harvard Kennedy School of Government, National Defense force Academy (NDU), and the Asia Pacific Center for Security Studies (APCSS). Currently, she is working on two book projects, i on the topic of 'Ethnic Narratives', to exist published past Oxford University Press, and the other on the topic of 'Dandy Power Ambitions" to be published past Lexington Press, an banner of Rowman and Littlefield.
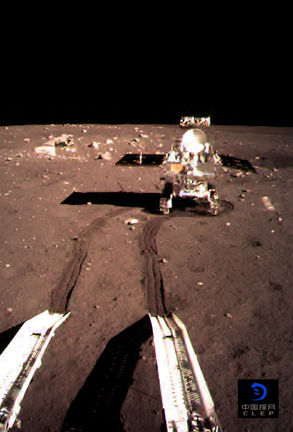
The China National Space Assistants (CNSA) – Chang'east iv mission landed on the dark side of the moon. Yutu-two ("Jade Rabbit-ii") rover disembarked from the lander to begin exploring the lunar surface. Photo courtesy CNSA.
Outer-space is irresolute given the visible and growing discourse in developed nations about trillions of dollars of infinite-based resources, waiting to exist harvested, to include Platinum, Titanium, Solar Power.
This discourse is a departure from the Cold State of war 'Infinite Race' betwixt the U.South. and the U.S.S.R, when getting somewhere first in infinite was critical for purposes of prestige and reputation.[1] Today, the space discourse aims to develop competence in technology to generate profit by investing in hereafter projects similar Space-based Solar Power (SBSP), asteroid mining, and lunar presence. Space is becoming as much a individual sector enterprise as it is state driven. U.S. based companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, Planetary Resources, Deep Infinite Industries, Chinese-based companies like OneSpace, Tencent, LandSpace, and Indian based companies like ReBeam, Bellatrix, TeamIndus, Astrome, are pushing for legislation that enables individual sector investments in infinite
Consequently, the U.Southward. Congress passed the "U.S. Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Human activity" in 2015, offering its citizens ownership over space resources on a 'first come, get-go serve' principle.[two] In China, there is interest in establishing similar legislation. India released its draft "Space Utilities Pecker" in 2017 to regulate and encourage individual investments.[3] Significantly, China is investing in space resource capabilities similar asteroid mining, SBSP, especially aimed at making China the virtually advanced country in space applied science by 2045.[4] India follows close backside, with its former President Abdul Kalam stating that but after harvesting space resource can Bharat truly develop. In 2018, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi committed India to a homo space program aimed at accomplishing feats leading to permanent space presence.[5]
With Commerce follows War machine Innovation
History informs usa that commerce led to military innovation for maintaining gratuitous access and safe passage. The development of the British Purple Navy and the U.S. Navy, including the reestablishment of the Marine Corps, whose principal task was to fight the Barbary pirates in Tripoli and Algiers, reflects this.[6] With growing commercial interests and military assets in space, Chinese President Eleven Jingping directed China's Strategic Support Force (SSF), established in 2015, tasked with 'space and cyber', to innovate and develop to back up Prc's growing presence in space.[seven] In response, U.S. President Donald Trump announced the establishment of a 'U.S. Space Force' in June 2018, to respond to the ascent challenges of space dominance/industrialization, and military innovations by China and Russia.[8] The Pentagon released a report soon subsequently, detailing how the 'Space Force' will be established.[9] The absence of clear regulatory frameworks, anticipating this space-based economy, implies the need for additions to the 1967 Outer Space Treaty (OST) that does not offer clear provisions in this regard. Luxembourg is the only land to found legislation to regulate asteroid mining and create a sovereign fund that can attract private space companies to set up shop.[10] Still, to argue that this growing economic contest would pb to militarization of outer-space is missing the point. Space is already militarized with military infinite satellites, Inter-Continental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) paths, and Anti-Satellite Weapons (ASAT) engineering. Wang Cheng, a Chinese intellectual, noted in an commodity titled, "The United states of america Armed forces's 'Soft Ribs,' A Strategic Weakness," in 2000 that, "For countries that can never win a war with the U.South. past using the method of tanks and planes, attacking the U.S. space system may be an irresistible and nearly tempting choice."[11] China's 2007 ASAT test (a decade agone), alerted the globe to potential Chinese threats to their satellites.
Significantly, the OST ensures that "States shall non place nuclear weapons or other weapons of mass destruction in orbit or on angelic bodies or station them in outer space in any other manner'.[12]

Photo Pixabay.com
While the OST states that "Outer space, including the moon and other celestial bodies, is not subject area to national appropriation past merits of sovereignty, by means of use or occupation, or by whatever other means,"[13] information technology also affirms in article ane that "Outer space, including the moon and other celestial bodies, shall exist complimentary for exploration and use by all States…"[14] and farther requires that "The activities of non-governmental entities in outer space, including the moon and other celestial bodies, shall require authorization and continuing supervision by the appropriate State Party to the Treaty…" [fifteen] In that context, the U.Due south. claims that asteroid mining constitutes but 'use' and involves no claim of sovereignty over either space or a celestial body. To comply with the provision of authorization and continuing supervision, the U.Southward. Congress has written laws stating, "A United States denizen engaged in commercial recovery of an asteroid resources or a space resource nether this affiliate shall be entitled to whatsoever asteroid resource or space resource obtained, including to possess, own, transport, use, and sell the asteroid resources…"[16] Similarly, Luxembourg's law states, "authorisation shall be granted to an operator for a mission of exploration and employ of space resources for commercial purposes upon written application to the ministers."[17] The International Establish of Space Police force Position Paper states, "Therefore, in view of the absence of a clear prohibition of the taking of resources in the Outer Infinite Treaty one tin conclude that the use of infinite resources is permitted. Viewed from this perspective, the new U.s.a. Act is a possible interpretation of the Outer Space Treaty. Whether and to what extent this interpretation is shared by other States remains to be seen."[18]
That said, disharmonize could break out if two countries (say U.Due south. and Cathay) arrive at an asteroid rich in resources and claim ownership based on 'first come, first serve'. What then?[19] At that place is no established regulatory authority that can adjudicate in such a dispute. Nosotros know that the U.S. military is constitutionally obligated to come to the assistance of U.South. military and commercial avails if it is threatened by an antagonist. The U.Due south. Commercial Act said every bit much, "It is the sense of Congress that the Department of Defense plays a vital and unique office in protecting national security assets in space."[20] The lack of legal clarity in these matters requires urgent intervention every bit the position of the U.S., Luxembourg is disputed by some. The United nations Function for Outer Infinite Affairs (UNOOSA) should brainstorm the process of adding protocols to the OST, perchance in line with The Hague International Infinite Resource Governance Working Group's typhoon proposal,[21] given the big-scale entry of the private sector into space. We must avoid repeating the mistakes of the by when individual trading organizations similar the Dutch East India Company and the British East India Company undertook excessive commercial exploitation, without any regulatory mechanisms in identify, to the destruction of the colonies. Ideas of infinite colonization is relevant here equally policy makers have framed the discourse as such. For instance, Ye Peijian, caput of Prc's Lunar Mission stated that [t]he universe is an ocean, the moon is the Diaoyu Islands, Mars is Huangyan Isle. If we don't go at that place now even though we're capable of doing and so, then we will be blamed by our descendants. If others get there, then they volition take over, and you lot won't exist able to go fifty-fifty if yous want to. This is reason enough.[22] Elon Musk, founder of SpaceX has pushed for plans to colonize Mars stating, "It's important to get a self-sustaining base of operations on Mars considering it'due south far enough away from earth that [in the effect of a war] information technology's more probable to survive than a moon base."[23]
In this context, countries like UAE and Grand duchy of luxembourg can influence regime construction that ensures that 'Middle Powers'[24] have advantage of the future space economy. I ascertain Middle Powers equally those states in the international system that locate beneath a super-power or a major power, but with enough ability, capacity and influence at their disposal to shape international regimes and events. These powers utilize their constitutive capacities, especially through their strange policy beliefs, to not only create global norms and standards of beliefs, but as well add legitimacy to international regimes through their back up. In my interpretation, both UAE and Grand duchy of luxembourg are Middle Powers. The role of Middle Powers is likely to grow in the realm of outer-space. After all, the U.S. commercial act does privilege, "starting time come up, beginning serve", with an implicit assumption that those who arrive starting time will be American citizens. Hence, the cardinal question is how to develop a framework that ensures turn a profit sharing of a global mutual, given the range of resources in outer-space.
UAE and Luxembourg
While Great Ability (U.S, People's republic of china, India) deportment may be primary drivers on space, their deportment take place against a tapestry of institutions, norms and receive blessing or approbation of a larger international social club which may make up one's mind the legitimacy or illegitimacy of such actions. Every bit Middle Powers, both UAE and Luxembourg appreciate the possibility of space resources to shift resource availability and command with implications for changes in global power.[25] Each is constructing their approach to this under-governed and contested region according to their own unique cultural context and preferences.
UAE
In 2014, UAE announced the establishment of its space bureau with the explicit aim to develop UAE as the regional hub for outer space activities in the Middle-East.[26] The UAE Infinite Bureau seeks to help resolve global bug of natural disasters and share space expertise to mitigate the problems arising from shrinking resources and climate modify. The Mohammad Bin Rashid Infinite Center (MBRSC), the commercial satellite communication companies, Thuraya and Al Yah Sat, are taking the lead in this domain. Past end of 2019, the UAE Infinite Bureau and Exolaunch will jointly launch the MeznSat, a satellite developed past students from the American Academy of Ras Al Khaimah and Khalifa University. MeznSat volition monitor and measure out the methane and carbon dioxide levels in the UAE's atmosphere.[27] Co-ordinate to Dr Mohammed Al Ahbabi, the Managing director General of the UAE Space Bureau "The MeznSat project falls within the framework of the UAE Space Bureau'southward strategy, which aims to develop Emirati capacities and expertise and back up scientific research".[28]
 One of UAE's major space project is its Mars Mission, named "Hope Probe", an indigenously congenital spacecraft that will orbit MARS and study its climate and temper by 2021.[29] 2021 is significant for the UAE as it marks the 50th year of its institution, and the Hope Probe is planned to utilize space in that celebration. On Apr 22, 2019, the UAE Space Bureau and the MBRSC issued a statement that the Promise Probe was 85 per cent complete. Managing director-General of the MBRSC, Yousuf Hamad Al Shaibani, asserted that, "Completing 85 per cent of the Hope Probe in this brusk catamenia was a bully challenge that we overcame through the guidance of our wise leadership and the efforts of our youth. The UAE has reached an advanced phase in achieving our wise leadership's vision to attain the Mars orbit by December 2021".[xxx]
One of UAE's major space project is its Mars Mission, named "Hope Probe", an indigenously congenital spacecraft that will orbit MARS and study its climate and temper by 2021.[29] 2021 is significant for the UAE as it marks the 50th year of its institution, and the Hope Probe is planned to utilize space in that celebration. On Apr 22, 2019, the UAE Space Bureau and the MBRSC issued a statement that the Promise Probe was 85 per cent complete. Managing director-General of the MBRSC, Yousuf Hamad Al Shaibani, asserted that, "Completing 85 per cent of the Hope Probe in this brusk catamenia was a bully challenge that we overcame through the guidance of our wise leadership and the efforts of our youth. The UAE has reached an advanced phase in achieving our wise leadership's vision to attain the Mars orbit by December 2021".[xxx]
Interestingly, the UAE infinite program is advertised as the "get-go Arab, Islamic probe to reach MARS by encouraging the peaceful awarding of space research".[31] Minister of State for College Education and Advanced Skills and Chairman of the UAE Space Agency, Dr Ahmad Belhoul Al Falasi specifies:
The UAE is on the verge of making history, after turning its dream of becoming the start Arabic and Islamic state to send a spacecraft to Mars into reality. This awe-inspiring endeavour is the culmination of the efforts of a skilled and experienced team of young Emiratis who, with the support of the nation and its visionary leadership, volition secure the UAE'south position at the forefront of space exploration.[32]
Co-ordinate to the UAE's Ambassador to the The states, Yousef Al Otaiba, "This is the Arab world'due south version of President Kennedy's Moon shot – it'due south a vision for the future that can engage and excite a new generation of Emirati and Arab youth".[33] In October 2015, the UAE infinite agency became a fellow member of the International Space Exploration Coordination Group (ISECG).[34] Dr. Mohammed Al Ahbabi, Director General of the UAE Space Agency, specifies, "certain countries might have problems hither on Earth, but y'all will see them cooperate in space".[35] UAE is starting to play a prominent function in the United nations's Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) and by hosting several international meetings and conferences on space law and policy. Through its membership in ISECG and U.N. space forums, the UAE tin can bring almost substantial influence to construct this future space regime relevant to a resource-based hereafter of space, especially to ensure that future is based on cooperation.
In March 2019, the UAE adopted its National Space Strategy 2030, in a meeting chaired by Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice President and Prime Minister of the UAE and Ruler of Dubai. The National Space Strategy 2030 is ambitious, and it includes investments on infinite manufacturing, associates, infinite scientific discipline and research, besides as commercial space. Critically, the UAE also commited to establish a infinite regulatory framework, which includes four components: National Space Policy, Space Sector Constabulary, Space Regulations, and National Space Strategy.[36]
Luxembourg
Luxembourg'due south prominence in encouraging exploitation of space resource is growing. In June 2016, Luxembourg established a $227 million fund to concenter companies focused on asteroid mining.[37] It became the beginning European country to develop a legal framework (like the 2015 US Asteroid Act) to adjudicate the commercial exploitation of space resource. In 2016, its Ministry of Economy announced the establishment of the Space Resources Initiative (SRI), whose role "will exist the development of a legal and regulatory framework confirming certainty nigh the future ownership of minerals extracted in space from Near Earth Objects such as asteroids."[38] The SRI website states that Luxembourg aims to establish itself as a European hub (similar to UAE's goal for the Middle-East), in the "exploration and utilize of infinite-based resources".[39] Luxembourg has a typhoon law that states that companies can keep the resources they accept mined. This positive atmosphere has drawn asteroid mining companies like U.South. based Deep Infinite Industries, Planetary Resources and Japanese company, iSpace, developing lunar landers, to open shop in Luxembourg. Luxembourg is already cooperating with Deep Space Industries (at present re-branded as Bradford Infinite Inc. after it was bought up past Bradford Space) on its Prospector X mission that aims to use a nano-spacecraft to examination its asteroid technologies. To add to its institutional chapters, Luxembourg established its Space Agency on September 12, 2018, specially aimed at Space Resources. Deputy Prime Government minister and Government minister of the economy, Étienne Schneider, appear that "The agency volition exist well-equipped to back up industry in their daily challenges, and it leads to the most favorable surroundings for this sector to continue to abound".[40] He announced the creation of $116 one thousand thousand Grand duchy of luxembourg Infinite Fund. In May 2019, Luxembourg and the U.Due south. signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to deepen cooperation on tackling infinite debris, defence, space commerce and regulation. Significantly, Luxembourg has signed space cooperation agreements with China, Japan, UAE, Brazil, Poland, Belgium, the Czech Republic.[41]
Luxembourg'due south penchant for understanding the lucrative nature of outer space was vindicated by its early on intervention in communication satellites. In the 1980s, when the space commercial satellite manufacture was still in its early days, Luxembourg passed legislations and invested heavily in its homegrown space visitor, Société Européenne des Satellites (SES), which enabled it to thrive and enjoy revenues to the tune of 2 billion Euros in 2015.[42] Consequently, Luxembourg is taking deliberate constitutive actions, contextually situated within the futuristic space-resources discourse, taking advantage of its state capacity rooted in high Gross domestic product Per Capita growth rates ($104, 103.00).[43]
The question that bears some significance is: In this scenario of growing interest in infinite industrialization, mining, and infinite presence, how tin can countries like Grand duchy of luxembourg and UAE ensure shared benefits from the futurity space economic system?
Hither are a few recommendations: –
- Lead the earth in passing progressive national space law to establish compatible norms for infinite resources.
- Organize global majuscule through big investment funds and bank loans for infinite development.
- Organize global talent through innovation prizes (as is happening through the UAE's UAV and infinite challenges).
- Offer to host global organizations for space governance (the Space Equivalent of the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) to ensure safe of navigation,
- Space governance issues such equally agile debris removal, insurance reform, space traffic direction, and frequency and slot allocation for Solar Power Satellites are likely to be ill-perceived if initiated by whatsoever of the major spacefaring powers, simply if initiated and moderated by Middle Powers, competition between the Major Powers can be managed.
- Level up Grand duchy of luxembourg and UAE's make in renewable energy past investing in ideas like Space Based Solar Ability.
Interestingly, very similar to China employing its space program as a disquisitional function of its Prc dream, and ambitions of utilizing space for the 100th yr ceremony of the institution of the People'due south Democracy of China (PRC) – 2049, UAE is broadcasting its Mars program as a celebration of the lth yr of its establishment (2021). Curiously enough, 2021 is also the year that Cathay will utilize space to gloat the 100th yr establishment of the Communist Party of China (CPC).[44] What I notice fascinating in these narratives that space achievements especially those that seek infinite industrialization and space commerce are broadcasted as celebratory projects by this major and middle infinite powers.
The game has changed: from the days of Apollo and Sputnik, when getting somewhere offset in space and then returning to world, was viewed as offer smashing prestige. We are in the historic period of Chang'east four: when achieving infinite presence and industrialization are seen as offering swell economical benefits and the resultant prestige that comes with that.
1Robert Hackett, "Asteroid Passing Close to Earth Could Contain $5.4 Trillion of Precious Metals", Fortune, July 20, 2015 at http://fortune.com/2015/07/xx/asteroid-precious-metals/ (accessed September 14, 2018).
[2] "U.S. Commercial Space Launch Competitiveness Deed, 2015," H.R. 2262, 114th Cong, 2015-2016 at https://www.congress.gov/neb/114th-congress/house-bill/2262/text (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[iii] Aswathi Pacha, "The Hindu Expalins: What is the Space Activities Neb, 2017", The Hindu, Nov 23, 2017 at https://world wide web.thehindu.com/sci-tech/scientific discipline/the-hindu-explains-what-is-the-space-activities-neb-2017/article20680984.ece (Accessed September xiv, 2018).
[iv] Mia Chi, "China Aims to be World-Leading Space Power by 2045", People's republic of china Daily, November 17, 2017 at http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2017-11/17/content_34653486.htm (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[5] Michael Safi, "India Aims to Send Astronauts into Space by 2022, Modi Says", The Guardian, August 15, 2018 at https://www.theguardian.com/world/2018/aug/15/india-conduct-manned-space-mission-2022-modi (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[half dozen] For more, Max Boot, The Roughshod Wars of Peace Pocket-sized Wars and the Ascent of American Power (New York: Basic Books, 2002), pp. iii-29.
[7] Xinhua, "Strive to Build a Stiff, Mod Strategic Support Force: Eleven," ChinaMilitary, Aug. 29, 2016, http://eng.chinamil.com.cn/view/2016-08/29/content_7231309.htm.
[8] Namrata Goswami, "The US 'Infinite Strength' and its Implications", The Diplomat, June 22, 2018 at https://thediplomat.com/2018/06/the-us-infinite-force-and-its-implications/ (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[ix] "Last Report on Organizational and Management Structure for the National Security Space Components of the Department of Defence," Section of Defence, Aug. 9, 2018, at https://media.defense force.gov/2018/Aug/09/2001952764/-i/-ane/1/ORGANIZATIONAL-MANAGEMENT-STRUCTURE-DOD-NATIONAL-SECURITY-SPACE-COMPONENTS.PDF (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[10] Jeff Foust, "Grand duchy of luxembourg Adopts Space Resources Law", SpaceNews, July 17, 2017 at https://spacenews.com/grand duchy of luxembourg-adopts-space-resource-law/ (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[11] Marker Williams Pontin, "China's Antisatellite Missile Test: Why?" MIT Applied science Review, March eight, 2007, https://www.technologyreview.com/south/407454/chinas-antisatellite-missile-exam-why/.
[12] "Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Infinite, Including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies", at http://www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/ourwork/spacelaw/treaties/introouterspacetreaty.html (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[xiii] Ibid.
[14] Ibid.
[15] Ibid.
[sixteen] "U.S. Commercial Infinite Launch Competitiveness Deed, 2015," n.two.
[17] "Typhoon Constabulary on the Exploration and Utilise of Space Resource", Luxembourg, at https://spaceresources.public.lu/content/dam/spaceresources/news/Translation%20Of%20The%20Draft%20Law.pdf (Accessed September 17, 2018).
[xviii] International Institute of Infinite (IISL)"Position Paper on Space Resources Mining", Dec xx, 2015, p.3 at http://iislwebo.wwwnlss1.a2hosted.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/SpaceResourceMining.pdf (Accessed September sixteen, 2018) ; IISL, Advisers of Studies, "Does International Space Constabulary Either Let of Prohibit the taking of Resource in Outer Space and on Celestial Bodies and How is This Relevant for National Actors? What is the Context, and What are the Contours and Limits of this Permission or Prohibition?", Background Paper, 2016 at http://iislweb.org/docs/IISL_Space_Mining_Study.pdf (Accessed September 16, 2018).
[19] Namrata Goswami, "Star Wars From Space-Based Solar Power to Mining Asteroids for Resources: China'due south Plans for the Final Frontier", Policy Forum, September 7, 2016 at https://world wide web.policyforum.net/star-wars/ (Accessed September fourteen, 2018).
[twenty] "U.South. Commercial Infinite Launch Competitiveness Act, 2015," due north.2.
[21] "The Hague International Space Resources Governance Working Group", University of Leiden, https://www.universiteitleiden.nl/en/law/institute-of-public-constabulary/institute-for-air-space-law/the-hague-space-resource-governance-working-grouping (Accessed September 16, 2018).
[22] "Space: The Adjacent South China Sea," Maritime Executive, July thirteen, 2018, https://www.maritime-executive.com/editorials/infinite-the-adjacent-due south-china-bounding main#gs.8SP=u7U.
[23] Olivia Solon, "Elon Musk: Nosotros Must Colonize Mars to Preserve our Species in a Third Earth State of war", The Guardian, March xi, 2018 at https://world wide web.theguardian.com/applied science/2018/mar/eleven/elon-musk-colonise-mars-third-world-war (Accessed on September 16, 2018).
[24] For an interesting perspective on Middle Powers, delight see Eduard Jordaan, "The Concept of a Middle Power in International Relations: Distinguishing Between Emerging and Traditional Middle Powers", Politikon: South African Journal of Political Studies, xxx (1), 2003, 165-181 at https://ink.library.smu.edu.sg/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1393&context=soss_research (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[25] "Luxembourg and the United Arab Emirates Sign MoU on Space Resources", Infinite Resource.Lu, October 10, 2017 at https://spaceresources.public.lu/en/actualites/2017/MoU-UAE.html (Accessed September xiv, 2018).
[26] Muhammad Bin Rashid Space Center, at https://mbrsc.ae/en/page/aboutus (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[27] Jack Dutton, "UAE Infinite Agency to Launch Satellite Adult by Students", The National, May 12, 2019 at https://www.thenational.ae/uae/scientific discipline/uae-space-agency-to-launch-satellite-developed-past-students-1.860640 (Accessed on May xiii, 2019).
[28] Ibid.
[29] "Emirates Mars Mission," UAE Space Agency, at http://www.emiratesmarsmission.ae/mars-probe (Accessed September xiv, 2018).
[30] "Video: UAE'south Promise Probe Bound for Mars is 85 per cent complete", The Khaleej Times, April 24, 2019 at https://world wide web.khaleejtimes.com/news/full general/video-uaes-hope-probe-bound-for-mars-is-85-consummate- (Accessed on May 13, 2019).
[31] Muhammad Bin Rashid Space Centre, n.26.
[32] "Video: UAE'due south Hope Probe Bound for Mars is 85 per cent consummate", n.30.
[33] Taimur Khan, "Mars Mission 'Arab World's Kennedy Moon Shot', Says UAE", The National, December iii, 2015 at https://world wide web.thenational.ae/earth/mars-mission-arab-world-s-kennedy-moon-shot-says-uae-ambassador-to-u.s.a.-1.103660 (Accessed on September xiv, 2018).
[34] "International Infinite Exploration Coordination Group, "Annual Report 2015", at https://www.dlr.de/Portaldata/28/Resources/dokumente/rm/ISECG_AnnualReport_2015.pdf (Accessed September xiv, 2018).
[35] Thamer Al Subaihi, "UAE Space Plan a Conduit for Cooperation", The National, November 28, 2015 at https://www.thenational.ae/uae/uae-space-plan-a-conduit-for-cooperation-one.67069 (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[36] "UAE Cabinet Approves National Space Strategy 2030", Khaleej Times, March 12, 2019 at https://www.khaleejtimes.com/news/government/uae-chiffonier-approves-national-space-strategy-2030–12 (Accessed on May 13, 2019). Besides see National Infinite Strategy 2030 at https://world wide web.government.ae/en/almost-the-uae/strategies-initiatives-and-awards/federal-governments-strategies-and-plans/national-space-strategy-2030 (Accessed on May 13, 2019).
[37] David Z. Morris, "Luxembourg to Invest $227 One thousand thousand in Asteroid Mining", Fortune, June 5, 2016 at http://fortune.com/2016/06/05/luxembourg-asteroid-mining/ (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[38] "Space Resources.Lu", at https://spaceresources.public.lu/en.html (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[39] Ibid.
[40] Jeff Foust, "Luxembourg Establishes Infinite Agency and New Fund", SpaceNews, September 13, 2018 at
[41] "Grand duchy of luxembourg and Us Agree to Deepen Cooperation in Space", Phys.org, May 10, 2019 at https://phys.org/news/2019-05-luxembourg-deepen-cooperation-space.html (Accessed on May 13, 2019).
[42] Atossa Araxia Abrahamian, "How a Revenue enhancement Haven is Leading the Race to Privatise Space", The Guardian, September 15, 2017 at https://www.theguardian.com/news/2017/sep/15/luxembourg-tax-haven-privatise-infinite (Accessed September 14, 2018).
[43] The World Bank, "GDP Per Capita (Current US$), at https://information.worldbank.org/indicator/ny.gross domestic product.pcap.cd (Accessed September fourteen, 2018).
[44] "China in the New Era: What to Await in 2021?", Global Times, Dec 10, 2017 at http://www.globaltimes.cn/content/1079510.shtml (Accessed on May 13, 2019).
© Dr Namrata Goswami
Source: https://liveencounters.net/2019-le-mag/06-june-2019/dr-namrata-goswami-the-competition-for-outer-space-resources/
Postar um comentário for "Felix Whelan Content Uploads 2014 Genuflect 2"